Molybdenum Removal Wastewater Test
Key Points of Recent Amendments and Additions to the Effluent Discharge Standards (4/8)
The Environmental Protection Administration of the Executive Yuan amended and announced on December 25, 2017, that starting from 2021 (next year), some control items of the effluent discharge standards will be tightened and new ones will be added. Based on improving water body quality and reducing the risk of agricultural land pollution, control items and limits such as ammonia nitrogen, heavy metals, carcinogenic substances, and true color chroma have been amended.
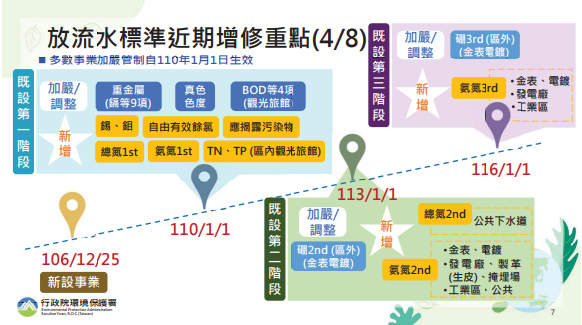
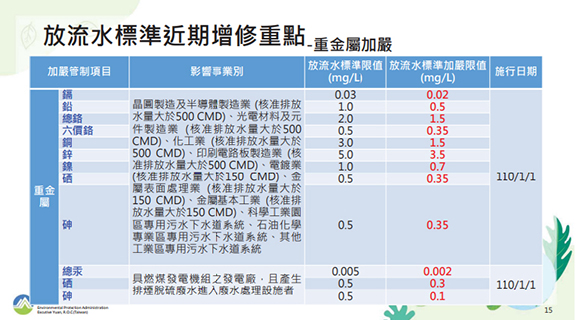
Key Points of Recent Amendments and Additions to the Effluent Discharge Standards - Tightening and Newly Added Heavy Metals
Implemented in stages - Tighten the control limits of 9 heavy metals including cadmium, lead, total chromium, hexavalent chromium, copper, zinc, nickel, selenium, and arsenic, and add control items such as tin and molybdenum.
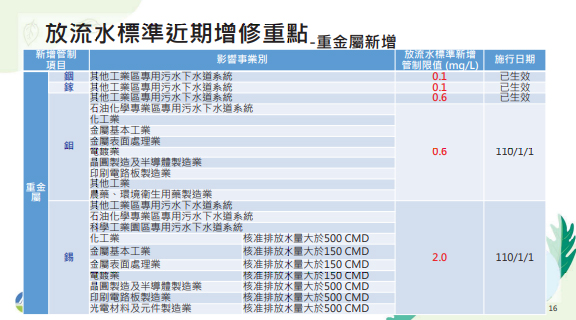
In order to further improve the overall water quality in Taiwan, reduce the amount of pollution borne by water bodies, and improve river water quality. The Environmental Protection Administration of the Executive Yuan tightened regulations and added regulations for some specific industries in 2024 and 2027. Detailed control items can be viewed on the website of the Environmental Protection Administration of the Executive Yuan.
Experiment on Molybdenum Removal from RM Wastewater in a Steel Plant
I. Problem Discussion
According to a steel plant in the south, there is a problem that the molybdenum content in the RM wastewater effluent from the plant exceeds the discharge standard.
On May 12, 2021, we went to understand the reasons and abnormal issues and took samples for molybdenum content analysis: 21 - 23 ppm. (The effluent discharge standard is 0.6 ppm), and the allowable discharge content gap is 35 times.
Given that molybdenum pollution in the plant is a frequent situation and is caused by the manufacturing process. We closely cooperated with the plant staff to discuss treatment methods.
Therefore, Kaiguang proposed: Physical Equipment Treatment Method
Physical Equipment Treatment Method:
Introduce the imported
Therefore, on May 17, Kaiguang cooperated with a steel plant in the south to conduct experimental tests on
In response to the increasingly tightened discharge standards, Kaiguang is also actively cooperating with many partner manufacturers. Regarding the problems that trouble customers, we assist in conducting relevant experiments and tests, and help customers plan wastewater treatment processes to meet regulatory standards in the future.
| Inspection Time | First Analysis on May 17 | Second Analysis on May 17 Adjusted Retention Time |
|---|---|---|
| Molybdenum Content | 2 ppm | 0.4 ppm |
II. Experimental Test of Molybdenum Metal Adsorption Catalyst
On May 17, 2021, the first test was conducted. The molybdenum content analysis of the raw water: 21 PPM
This test confirmed that this method can effectively remove molybdenum. However, due to the relatively dirty quality of the wastewater, containing oil and suspended solids, it is easy to cause catalyst blockage.
On May 18, 2021, a second test was conducted. The raw wastewater was filtered to remove oil and suspended solids, and the molybdenum content was continuously monitored. The molybdenum content of the raw water: 21 ppm, 23 ppm
From May 20 to May 24, a third test was conducted. The catalyst was backwashed, and the retention time was adjusted for continuous treatment and intermittent monitoring. The molybdenum content of the raw water: 21 ppm
| May 18 | May 20 | May 21 | May 24 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inspection Time / Molybdenum Content | |||||
| 08:40 / 1.7 ppm | 09:40 / 1.1 ppm | 11:40 / 0.8 ppm | 09:30 / 0.5 ppm | 09:30 / 0.5 ppm | 09:30 / 0.6 ppm |
| 13:30 / 1.5 ppm | 14:30 / 0.9 ppm | 15:40 / 0.8 ppm | 13:30 / 0.3 ppm | 13:30 / 0.7 ppm | 13:30 / 0.5 ppm |
| 16:40 / 0.4 ppm | 17:40 / 0.8 ppm | - | 17:30 / 0.4 ppm | 17:30 / 0.4 ppm | 17:30 / 0.5 ppm |
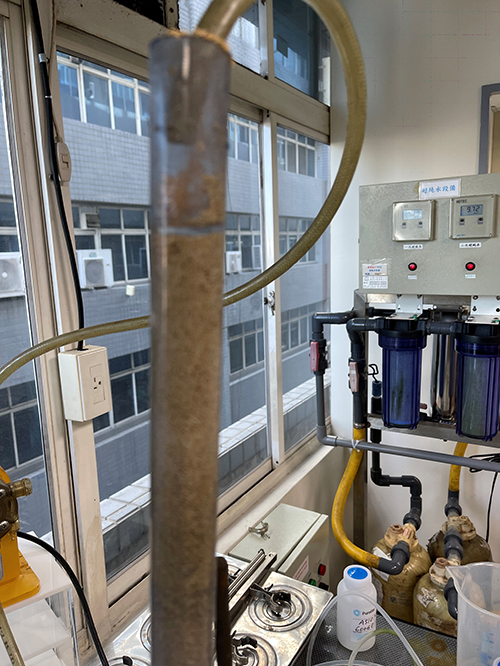
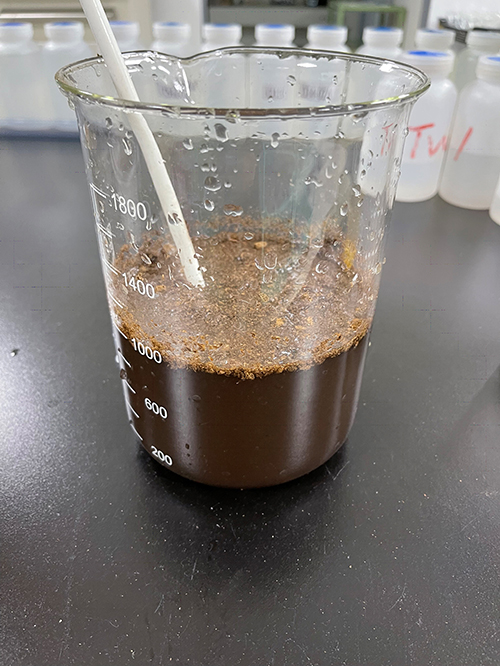
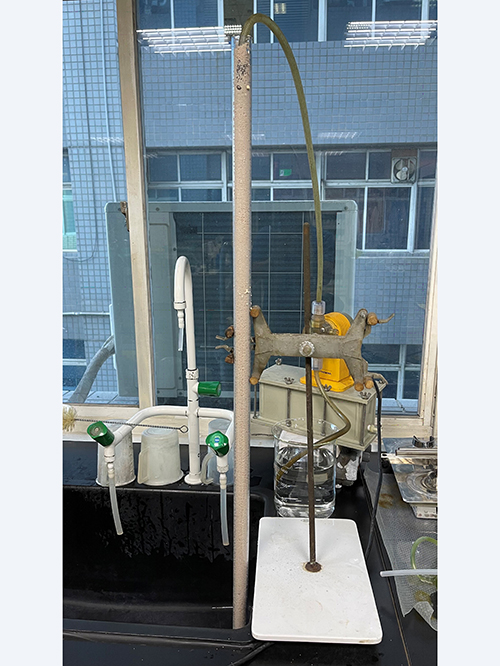



After the experimental test of the molybdenum metal adsorption catalyst, it has been determined that this is an executable physical treatment method. It can effectively remove molybdenum content to meet the discharge standard.
